

|
|
|
||||
|
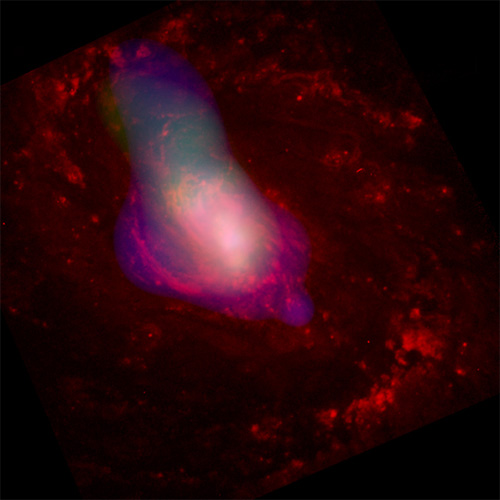
NGC 1068: An active galaxy about 50 million light years from Earth. (Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/MIT/UCSB/P.Ogle et al.; Optical: NASA/STScI/A.) Caption: A composite Chandra X-ray (blue/green) and Hubble optical (red) image of NGC 1068 shows hot gas blowing away from a central supermassive black hole at speeds averaging about 1 million miles per hour. The elongated shape of the gas cloud is thought to be due to the funneling effect of a torus, or doughnut-shaped cloud, of cool gas and dust that surrounds the black hole. The X-rays are scattered and reflected X-rays that are probably coming from a hidden disk of hot gas formed as matter swirls very near the black hole. Regions of intense star formation in the inner spiral arms of the galaxy are highlighted by the optical emission. Scale: Image is 36 arcsec on a side. Chandra X-ray Observatory ACIS/HETG Image
CXC operated for
NASA by the Smithsonian Astrophysical
Observatory
|
|
|