October 25, 2007
JPL Release:
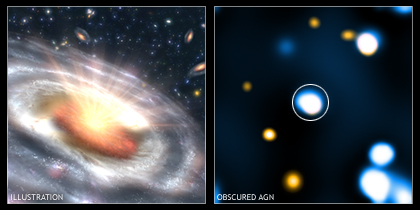
Credit: Illustration: NASA/JPL-Caltech; X-ray: NASA/CXC/Durham/D.Alexander et al.
Press Image and Caption
Astronomers have unmasked hundreds of black holes hiding deep inside dusty galaxies billions of light-years away
The massive, growing black holes, discovered by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space telescopes, represent a large fraction of a long-sought missing population. Their discovery implies there are hundreds of millions of additional black holes growing in our young universe, more than doubling the total amount known at that distance.
"Active, supermassive black holes are everywhere in the early universe," said Mark Dickinson of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory in Tucson, Ariz. "We had seen the tip of the iceberg before in our search for these objects. Now, we can see the iceberg itself." Dickinson is a co-author of two new papers appearing in the Nov. 10 issue of the Astrophysical Journal. Emanuele Daddi of the Commissariat a l'Energie Atomique in France led the research.
The findings are also the first direct evidence that most, if not all, massive galaxies in the distant universe spend their youths building monstrous black holes at their cores.
For decades, large populations of active black holes have been considered missing. These highly energetic structures, also called quasars, consist of a dusty, doughnut-shaped cloud that surrounds and feeds a growing supermassive black hole. They give off a lot of X-rays that can be detected as a general glow in space, but sometimes the quasars themselves can't be seen because dust and gas blocks their X-rays from our point of view.
"We knew from other studies from about 30 years ago that there must be more quasars in the universe, but we didn't know where to find them until now," said Daddi.
Daddi and his team initially set out to study 1,000 dusty, massive galaxies that are busy making stars, and were thought to lack quasars. The galaxies are about the same mass as our own spiral Milky Way galaxy, but irregular in shape. At 9 to 11 billion light-years away, they exist at a time when the universe was in its infancy, between 2.5 and 4.5 billion years old.
When the astronomers peered more closely at the galaxies with Spitzer's infrared eyes, they noticed that about 200 of the galaxies gave off an unusual amount of infrared light. X-ray data from Chandra, and a technique called "stacking," revealed the galaxies were in fact hiding plump quasars inside. The scientists now think that the quasars heat the dust in their surrounding doughnut clouds, releasing the excess infrared light.
"We found most of the population of hidden quasars in the early universe," said Daddi. Previously, only the rarest and most energetic of these hidden black holes had been seen at this early epoch.
For decades, large populations of active black holes have been considered missing. These highly energetic structures, also called quasars, consist of a dusty, doughnut-shaped cloud that surrounds and feeds a growing supermassive black hole. They give off a lot of X-rays that can be detected as a general glow in space, but sometimes the quasars themselves can't be seen because dust and gas blocks their X-rays from our point of view.
The newfound quasars are helping answer fundamental questions about how massive galaxies evolve. For instance, astronomers have learned that most massive galaxies steadily build up their stars and black holes simultaneously until they get too big and their black holes suppress star formation.
The observations also suggest that collisions between galaxies might not play as large a role in galaxy evolution as previously believed. "Theorists thought that mergers between galaxies were required to initiate this quasar activity, but we now see that quasars can be active in unharrassed galaxies," said co-author David Alexander of Durham University, United Kingdom.
"It's as if we were blind-folded studying the elephant before, and we weren't sure what kind of animal we had," added co-author David Elbaz of the Commissariat a l'Energie Atomique. "Now, we can see the elephant for the first time."
Consistent results were also recently obtained by Fabrizio Fiore of the Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma and his team. Their results will appear in the Jan 1, 2008, issue of Astrophysical Journal.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., manages the Chandra program for the agency's Science Mission Directorate. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations from the Chandra X-ray Center in Cambridge, Mass. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., manages the Spitzer Space Telescope mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. Science operations are conducted at the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology, also in Pasadena. Caltech manages JPL for NASA
For more information and graphics, visit:
http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu/spitzer
http://www.nasa.gov/spitzer
http://chandra.harvard.edu/
http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/main/
MEDIA CONTACTS
Whitney Clavin 818-354-4673
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.



