For Release: July 07, 2010
ESO
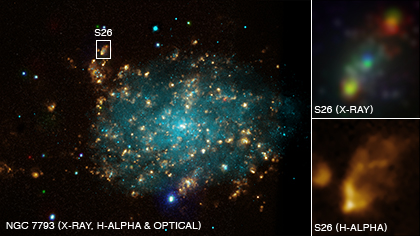
Credit: X-ray (NASA/CXC/Univ of Strasbourg/M. Pakull et al); Optical (ESO/VLT/Univ of Strasbourg/M. Pakull et al); H-alpha (NOAO/AURA/NSF/CTIO 1.5m)
Press Image and Caption
Combining observations made with ESO's Very Large Telescope and NASA's Chandra X-ray telescope, astronomers have uncovered the most powerful pair of jets ever seen from a stellar black hole. This object, also known as a microquasar, blows a huge bubble of hot gas, 1000 light-years across, twice as large and tens of times more powerful than other known microquasars. The discovery is reported this week in the journal Nature.
"We have been astonished by how much energy is injected into the gas by the black hole," says lead author Manfred Pakull. "This black hole is just a few solar masses, but is a real miniature version of the most powerful quasars and radio galaxies, which contain black holes with masses of a few million times that of the Sun."
Black holes are known to release a prodigious amount of energy when they swallow matter. It was thought that most of the energy came out in the form of radiation, predominantly X-rays. However, the new findings show that some black holes can release at least as much energy, and perhaps much more, in the form of collimated jets of fast moving particles. The fast jets slam into the surrounding interstellar gas, heating it and triggering an expansion. The inflating bubble contains a mixture of hot gas and ultra-fast particles at different temperatures. Observations in several energy bands (optical, radio, X-rays) help astronomers calculate the total rate at which the black hole is heating its surroundings.
The astronomers could observe the spots where the jets smash into the interstellar gas located around the black hole, and reveal that the bubble of hot gas is inflating at a speed of almost one million kilometres per hour.
"The length of the jets in NGC 7793 is amazing, compared to the size of the black hole from which they are launched," says co-author Robert Soria [1]. "If the black hole were shrunk to the size of a soccer ball, each jet would extend from the Earth to beyond the orbit of Pluto."
This research will help astronomers understand the similarity between small black holes formed from exploded stars and the supermassive black holes at the centres of galaxies. Very powerful jets have been seen from supermassive black holes, but are thought to be less frequent in the smaller microquasar variety. The new discovery suggests that many of them may simply have gone unnoticed so far. The gas-blowing black hole is located 12 million light-years away, in the outskirts of the spiral galaxy NGC 7793 (eso0914b). From the size and expansion velocity of the bubble the astronomers have found that the jet activity must have been ongoing for at least 200 000 years.
Note:
[1] Astronomers do not have yet any means of measuring the size of the black hole itself. The smallest stellar black hole discovered so far has a radius of about 15 km. An average stellar black hole of about 10 solar masses has a radius of about 30 km, while a "big" stellar black hole may have a radius of up to 300 km. This is still much smaller than the jets, which extend out to 1000 light-years, or about 9000 million million km!
More Information:
This result appears in a paper published in this week's issue of the journal Nature (A 300 parsec long jet-inflated bubble around a powerful microquasar in the galaxy NGC 7793, by Manfred W. Pakull, Roberto Soria and Christian Motch).
ESO, the European Southern Observatory, is the foremost intergovernmental astronomy organisation in Europe and the world's most productive astronomical observatory. It is supported by 14 countries: Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. ESO carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities enabling astronomers to make important scientific discoveries. ESO also plays a leading role in promoting and organising cooperation in astronomical research. ESO operates three unique world-class observing sites in Chile: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope, the world's most advanced visible-light astronomical observatory and VISTA, the world's largest survey telescope. ESO is the European partner of a revolutionary astronomical telescope ALMA, the largest astronomical project in existence. ESO is currently planning a 42-metre European Extremely Large optical/near-infrared Telescope, the E-ELT, which will become "the world's biggest eye on the sky".
Media contacts:
Manfred W. Pakull and Christian Motch
University of Strasbourg, France
Tel: +33 3 68 85 24 30, +33 3 68 85 24 28
Email: manfred.pakull@astro.unistra.fr, christian.motch@astro.unistra.fr
Roberto Soria
MSSL, University College London, UK
Tel:
Email: rsoria@physics.usyd.edu.au
Henri Boffin
ESO, La Silla, Paranal and E-ELT Press Officer
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6222
Cell: +49 174 515 43 24
Email: hboffin@eso.org



Visitor Comments (5)
Truly an amazing discovery. What I like the best is the explanation provided with the images. With the simplicity of the explanation, even an amateur student of Astrophysics can understand the strange events that occur in the universe. Thanks to NASA and the authors for spreading the knowledge.
Posted by Rajan Murkute on Wednesday, 11.24.10 @ 11:03am
I wont more pictures.
Posted by junaid on Sunday, 07.25.10 @ 04:02am
Thanks NASA, keep up the good work.
vin
Posted by vinpalkar on Friday, 07.16.10 @ 07:48am
Amazing and wonderful all your discoveries NASA. I would like to read more about black holes and quasars. Thank you very much.
Posted by Elena Morua on Friday, 07.9.10 @ 11:14am
Wow, truly awesomeness.
Posted by Evelyn on Friday, 07.9.10 @ 05:18am