The Chandra X-ray Observatory, launched on July 23, 1999, is part of NASA's family of "Great Observatories" that includes the Hubble Space Telescope, the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, and the Space Infrared Telescope Facility. As the world's premier X-ray observatory, Chandra gives astronomers a powerful new tool to investigate the hot regions of the universe where black holes, exploding stars, and colliding galaxies hold sway.
With its combination of four pairs of ultra smooth, high-resolution mirrors and efficient X-ray detectors, Chandra makes images at least thirty times sharper than any previous X-ray telescope. The High Resolution Camera, and the Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer record images electronically, and two transmission gratings enable scientists to make precise measurements of the energies of incoming X-rays.
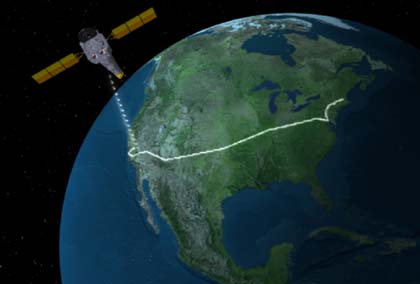
Communication between the Chandra Observatory and the Chandra Operations and Control Center is via the deep space network.
The Chandra X-Ray Observatory Center
The Chandra program, managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is an example of NASA's initiative to streamline the operations of its space science missions. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center (CXC), under the direction of Dr. Harvey Tananbaum, is located at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXC is responsible for planning the science observations based on proposals from the scientific community, processing data received from the observatory, and providing technical and scientific support to the scientists who use Chandra. The Center operates the observatory from its Operations & Control facility located at One Hampshire Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
The CXC is a collaboration of personnel from the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and the Chandra prime contractor, Northrop Grumman (NGST) of Redondo Beach, Calif., formerly TRW, Inc.
The Operations & Control Center (OCC) is staffed by the CXC, with the Flight Operations Team provided by NGST. The OCC has a glass-walled area outside the main control room where visitors and press can watch the Flight Operations Team and mission specialists as they communicate with the observatory and carry out the space flight operations.
Commands for executing the observation plan are transmitted from the OCC to one of three ground stations (in Spain, Australia, or California) that make up NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN). The DSN relays the commands to the orbiting spacecraft. The spacecraft carries out the commands and points the telescope to the specified targets, and moves the science instruments to their appropriate positions.
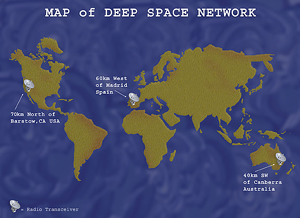
Map of the Deep Space Network, showing locations of radio telescopes in California, Spain, and Australia.
During routine operations, science data and monitoring data are sent from the spacecraft to the OCC, via the DSN, approximately every eight hours. Scientists and engineers use monitoring data to assess Chandra's condition. If the health or safety of the observatory appears to be in danger, the operating mode and the observation plans are modified.
Data from Chandra observations are processed at the Chandra Center. Observatory calibration data are made public as soon as possible. The scientific data belonging to guest observers and guaranteed time observers can be held by them for one year to allow time for analysis and publication of scientific results. The data are then placed in the public archive.
[ Press Index ] [ Fact Sheets ]




