E0102-72
 NASA/CXC/SAO NASA/CXC/SAOJpg (68 k) Tif (2.0 MB) PS (1.1 MB) |
E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light years of space, the multi-million degree source resembles a flaming cosmic wheel.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
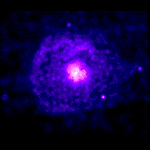
G21.5-0.9
 NASA/CXC/SAO NASA/CXC/SAOJpg (143 k) Tif (1.5 MB) PS (1.1 MB) |
The identification of G21.5-0.9 as the remnant of a supernova explosion is based on indirect evidence from radio and X-ray observations. At both radio and X-ray wavelengths, it appears as round patch in the sky. Detailed observations with radio telescopes confirm that the radio waves are produced by high energy electrons spiraling around magnetic field lines (synchrotron radiation). The X-rays are probably produced by the same process, but the electrons involved have energies many thousands times higher than those that produce the radio waves. The favored theory is that the high-energy electrons responsible for both the radio and X-ray emission are produced by a rapidly rotating, highly magnetized neutron star left behind when a massive star exploded some 40,000 years ago.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
PSR
0540-69  NASA/CXC/SAO NASA/CXC/SAOJpg (236 k) Tif (1.7 MB) PS (4.1 MB) |
PSR 0540-69 is a neutron star, or pulsar, that is rotating very rapidly, making a complete rotation every one-twentieth of a second. It is similar in many ways to the famous Crab Nebula pulsar. Both objects are spinning rapidly, are about 1,000 years old and are surrounded by a large cloud of gas and high-energy particles. The surrounding cloud in both cases is powered by the conversion of rotational energy of the neutron star into high energy particles through the combined action of rapid rotation and a strong magnetic field. PSR 0540-69 is 160,000 light years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one the Milky Way's small satellite galaxies.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
E0102-72
The Chandra X-ray Observatory image of E0102-72 reveals a roughly circular nebula floating against the deep black of space. The ring is glowing in bright blue-white tones with a mottled texture. Nestled inside this ring is some more texture and one strong and a couple faint wheel-like spokes. E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light years of space, the multi-million degree source resembles a flaming cosmic wheel.
G21.5-0.9
This Chandra X-ray Observatory image shows G21.5-0.9, a supernova remnant. A luminous nebula sits at the center of the image shining in intense fuchsia‑pink and violet tone. Surrounding it is a broad, diffuse halo in softer blue-purplish hues, stretching outward like a glowing mist. This outer halo has a mottled and gaseous texture with irregularities. Beyond that is a stark black background. The structure resembles a nested cosmic set—an inner electric nebula encased within a ghostly outer envelope. The identification of G21.5-0.9 as the remnant of a supernova explosion is based on indirect evidence from radio and X-ray observations. At both radio and X-ray wavelengths, it appears as a round patch in the sky. The favored theory is that the high-energy electrons responsible for both the radio and X-ray emission are produced by a rapidly rotating, highly magnetized neutron star left behind when a massive star exploded some 40,000 years ago.
PSR 0540-69
PSR 0540-69 is a rapidly rotating neutron star, or pulsar, making a complete rotation every one-twentieth of a second. The striking bright pink‑white point anchors the center is the energetic pulsar itself, a city-sized collapsed star emitting powerful X-rays. Around it, a curving arc or hook of amber‑orange glow sweeps outward, wispy tendrils against the pitch-black space. This object is about 1,000 years old and is surrounded by a large cloud of gas and high-energy particles. The surrounding cloud is powered by the conversion of rotational energy of the neutron star into high energy particles through the combined action of rapid rotation and a strong magnetic field. PSR 0540-69 is 160,000 light years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one the Milky Way's small satellite galaxies.




