Quasisoft Sources - Enigmatic X-ray Sources Point to Possible New Black Hole Population
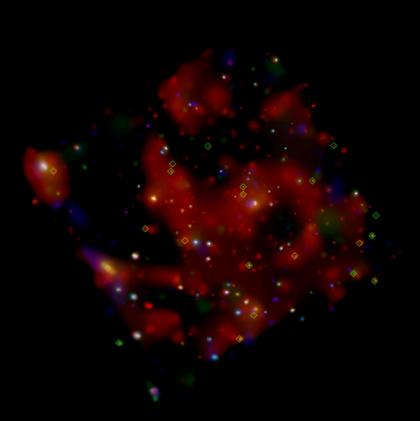
Chandra observations of the spiral galaxy M101 and several other nearby galaxies have revealed a possible new class of X-ray sources. These mysterious X-ray sources, marked with green diamonds in the image, are called "quasisoft" sources because they have a temperature in the range of one to four million degrees Celsius.
The power output of quasisoft sources is comparable to or greater than that of neutron stars or stellar-mass black holes fueled by the infall of matter from companion stars. This implies that the region that produces the X-rays in a quasisoft source is dozens of times larger.
One explanation is that these sources are produced by intermediate-mass black holes that have masses a hundred or more times greater than the mass of the Sun. Such objects would have much larger event horizons, which would account for the larger sizes and lower temperatures associated with the quasisoft sources. Alternatively, they could be standard neutron stars or stellar black holes where the associated region of hot gas is for some as yet unknown reason much larger than usual.
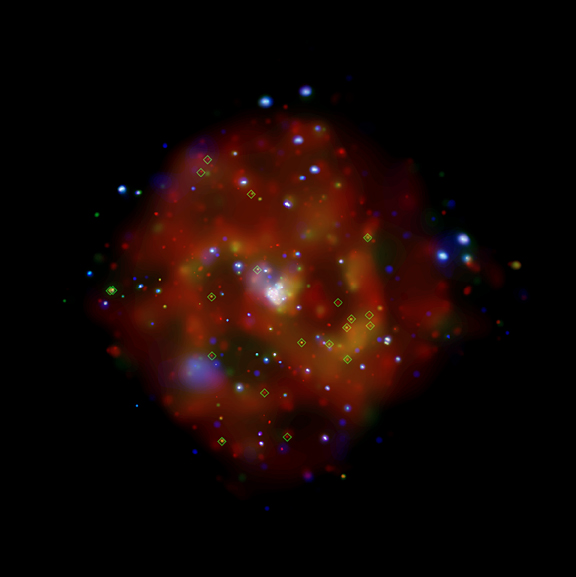

M83
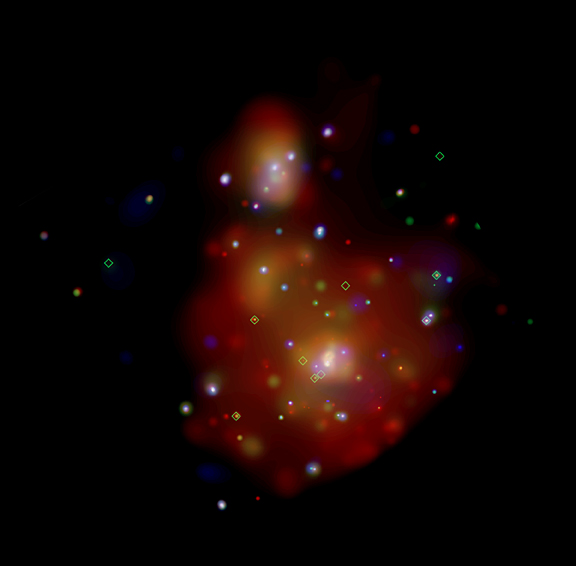

M51
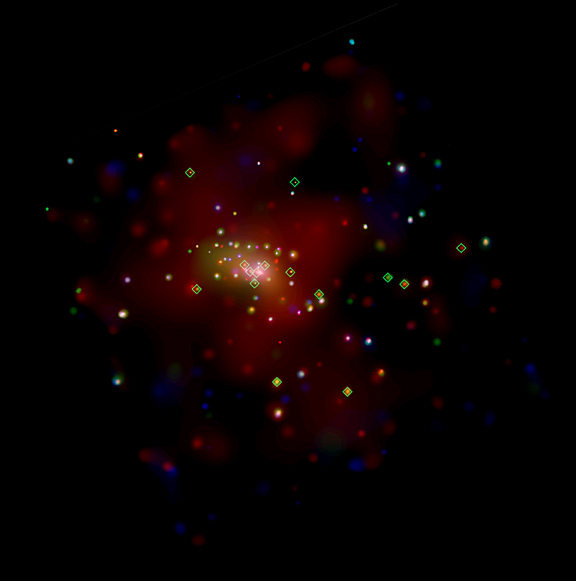

NGC 4697
"Hard" X-ray sources, such as neutron stars or stellar-mass black holes have temperatures greater than ten million degrees. The "supersoft" X-ray sources due to white dwarfs have temperatures of several hundred-thousand-degrees. A total of 72 quasisoft sources were discovered in the four galaxies: M101, M83, M51, and NGC 4697.
Until a few years ago, astronomers only knew of two sizes of black holes: stellar black holes with masses about ten times that of the Sun, and supermassive black holes located at the centers of galaxies, with masses ranging from millions to billions times that of the Sun. Recent evidence, however, suggests that a class of "intermediate-mass" black holes may also exist. Theories for the formation of intermediate-mass black holes involve the collapse of extremely massive stars, or the merger of many stellar-mass black holes.
As more quasisoft sources are discovered, the types of galaxies in which they reside and where they are located in a galaxy should give astronomers additional clues as to their nature and how they are formed. The present study indicates that quasisoft occur in various locations in elliptical as well as spiral galaxies.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Chandra X-ray Observatory image of spiral galaxy M101 resembles a fluffy-looking pinwheel. The dominant colors in the image are shades of dark red, blue, green, and orange. The image depicts a complex structure of the galaxy's various features in X-ray light, including its central bright core, vague spiral arms, and diffuse hot gas. Chandra observations of the spiral galaxy M101, as well as several other nearby galaxies (not pictured) have revealed a possible new class of X-ray sources. These mysterious X-ray sources, marked with about a dozen yellow-green diamonds spread throughout the image, are called "quasisoft" sources because they have a temperature in the range of one to four million degrees Celsius.