CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
Chandra X-ray Image of RCW 108
RCW 108 contains a cluster of young stars deeply embedded in a dark cloud. This molecular cloud, at a distance of about 4,000 light years from Earth, is in the process of being destroyed by intense radiation from hot and massive stars in a nearby star cluster outside the field of view. More than 400 X-ray sources were identified in Chandra's observations of RCW 108. About 90% of these X-ray sources are thought to be part of the cluster and not stars that lie in the field-of-view either behind or in front of it. Many of the stars in RCW 108 are experiencing the violent flaring seen in other young star-forming regions such as the Orion Nebula. Gas and dust blocks much of the X-rays from the juvenile stars located in the center of the image, explaining the relative dearth of Chandra sources in this part of the image.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/CfA/S.Wolk et al;)
RCW 108 contains a cluster of young stars deeply embedded in a dark cloud. This molecular cloud, at a distance of about 4,000 light years from Earth, is in the process of being destroyed by intense radiation from hot and massive stars in a nearby star cluster outside the field of view. More than 400 X-ray sources were identified in Chandra's observations of RCW 108. About 90% of these X-ray sources are thought to be part of the cluster and not stars that lie in the field-of-view either behind or in front of it. Many of the stars in RCW 108 are experiencing the violent flaring seen in other young star-forming regions such as the Orion Nebula. Gas and dust blocks much of the X-rays from the juvenile stars located in the center of the image, explaining the relative dearth of Chandra sources in this part of the image.
(Credit: NASA/CXC/CfA/S.Wolk et al;)
2
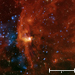
Spitzer Infrared Image of RCW 108
The Spitzer data of RCW 108 show the location of the embedded star cluster, which appears as the bright knot of red and orange just to the left of the center of the image. Some stars from a larger cluster, known as NGC 6193, are also visible on the left side of the image. Astronomers think that the dense clouds within RCW 108 are in the process of being destroyed by intense radiation emanating from hot and massive stars in NGC 6193.
(Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
The Spitzer data of RCW 108 show the location of the embedded star cluster, which appears as the bright knot of red and orange just to the left of the center of the image. Some stars from a larger cluster, known as NGC 6193, are also visible on the left side of the image. Astronomers think that the dense clouds within RCW 108 are in the process of being destroyed by intense radiation emanating from hot and massive stars in NGC 6193.
(Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Return to RCW 108 (October 06, 2008)