CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
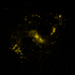
A Close-up View of NGC 4151
This image of NGC 4151 shows a close-up of the central region of the galaxy in an inset. The dimensions of the inset are only 2,000 light years across. Here, the Chandra X-ray data from the larger image are shown in blue, and we add in radio data from the VLA (purple) and HST data (yellow) showing oxygen emission. The linear structures show clear evidence for an earlier outburst from a supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
This image of NGC 4151 shows a close-up of the central region of the galaxy in an inset. The dimensions of the inset are only 2,000 light years across. Here, the Chandra X-ray data from the larger image are shown in blue, and we add in radio data from the VLA (purple) and HST data (yellow) showing oxygen emission. The linear structures show clear evidence for an earlier outburst from a supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
2
X-ray, Optical & Radio Images of NGC 4151
These images feature the central region of the spiral galaxy NGC 4151. In the pupil of the "eye," X-rays (blue) from Chandra are combined with optical data (yellow) showing positively charged hydrogen. The red around the pupil reveals neutral hydrogen detected by radio observations. A study has shown that the X-ray emission was likely caused by an outburst powered by the supermassive black hole located in the white region in the center of the galaxy. Evidence for this idea comes from the elongation of the X-rays running from the top left to the bottom right and details of the X-ray spectrum.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
These images feature the central region of the spiral galaxy NGC 4151. In the pupil of the "eye," X-rays (blue) from Chandra are combined with optical data (yellow) showing positively charged hydrogen. The red around the pupil reveals neutral hydrogen detected by radio observations. A study has shown that the X-ray emission was likely caused by an outburst powered by the supermassive black hole located in the white region in the center of the galaxy. Evidence for this idea comes from the elongation of the X-rays running from the top left to the bottom right and details of the X-ray spectrum.
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
3
Central Region of NGC 4151 with Scale Bar
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA)
4
NGC 4151 with Scale Bar
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA
(Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; Optical: Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope, Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA
NGC 4151 (March 10, 2011)