In commemoration of the 15th anniversary of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, four newly processed images of supernova remnants dramatically illustrate Chandra's unique ability to explore high-energy processes in the cosmos (see the accompanying press release).
The images of the Tycho and G292.0+1.8 supernova remnants show how Chandra can trace the expanding debris of an exploded star and the associated shock waves that rumble through interstellar space at speeds of millions of miles per hour. The images of the Crab Nebula and 3C58 show how extremely dense, rapidly rotating neutron stars produced when a massive star explodes can create clouds of high-energy particles light years across that glow brightly in X-rays.
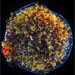
Tycho:
More than four centuries after Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe first observed the supernova that bears his name, the supernova remnant it created is now a bright source of X-rays. The supersonic expansion of the exploded star produced a shock wave moving outward into the surrounding interstellar gas, and another, reverse shock wave moving back into the expanding stellar debris. This Chandra image of Tycho reveals the dynamics of the explosion in exquisite detail. The outer shock has produced a rapidly moving shell of extremely high-energy electrons (blue), and the reverse shock has heated the expanding debris to millions of degrees (red and green). There is evidence from the Chandra data that these shock waves may be responsible for some of the cosmic rays - ultra-energetic particles - that pervade the Galaxy and constantly bombard the Earth.

G292.0+1.8:
At a distance of about 20,000 light years, G292.0+1.8 is one of only three supernova remnants in the Milky Way known to contain large amounts of oxygen. These oxygen-rich supernovas are of great interest to astronomers because they are one of the primary sources of the heavy elements (that is, everything other than hydrogen and helium) necessary to form planets and people. The X-ray image from Chandra shows a rapidly expanding, intricately structured, debris field that contains, along with oxygen (yellow and orange), other elements such as magnesium (green) and silicon and sulfur (blue) that were forged in the star before it exploded.

The Crab Nebula:
In 1054 AD, Chinese astronomers and others around the world noticed a new bright object in the sky. This “new star” was, in fact, the supernova explosion that created what is now called the Crab Nebula. At the center of the Crab Nebula is an extremely dense, rapidly rotating neutron star left behind by the explosion. The neutron star, also known as a pulsar, is spewing out a blizzard of high-energy particles, producing the expanding X-ray nebula seen by Chandra. In this new image, lower-energy X-rays from Chandra are red, medium energy X-rays are green, and the highest-energy X-rays are blue.

3C58:
3C58 is the remnant of a supernova observed in the year 1181 AD by Chinese and Japanese astronomers. This new Chandra image shows the center of 3C58, which contains a rapidly spinning neutron star surrounded by a thick ring, or torus, of X-ray emission. The pulsar also has produced jets of X-rays blasting away from it to both the left and right, and extending trillions of miles. These jets are responsible for creating the elaborate web of loops and swirls revealed in the X-ray data. These features, similar to those found in the Crab, are evidence that 3C58 and others like it are capable of generating both swarms of high-energy particles and powerful magnetic fields. In this image, low, medium, and high-energy X-rays detected by Chandra are red, green, and blue respectively.
Four different X-ray images from the Chandra X-ray Observatory of supernova remnants are shown in various colors including blue, purple, red, yellow and orange. The first image at upper left is the Crab Nebula in pale blue and orange. The overall structure of the Crab Nebula can be described as an irregularly shaped nebulous bell. In the Crab image, there is a bright, white dot in the center of the nebula, a complex network of filamentary structures that form a ring, as well as a jet. The upper center panel shows G292.0+1.8, a bright, glowing supernova remnant that resembles a jellyfish swimming on its side. The colors of the image are predominantly orange, white, yellow and blue, with some green and purple hues present. Next, in the upper right panel, is the Chandra image of Tycho's supernova remnant that reveals a glowing, multi-colored sphere that appears to be suspended in the blackness of space. This structure is actually a remnant of a massive explosion that occurred over 400 years ago, when the star underwent a catastrophic event known as a supernova. The colors of the remnant have a slightly rainbow-like appearance, with blue, green, orange, yellow and purple hues dominating the image. The texture of the remnant can be described as somewhat mottled or uneven, with areas of varying brightness and contrast throughout the sphere, like bits of material are jumping out towards the viewer. Finally, the bottom panel shows 3C58 in a wash of blue, red and violet, with intricate texture making up the remnant. There is one central, noticeable bright spot in the image, with loops and protrusions around it. The overall shape of the supernova remnant is irregular, with a croissant-like structure. Overall, the images of the Tycho and G292.0+1.8 supernova remnants show how Chandra can trace the expanding debris of an exploded star and the associated shock waves that rumble through interstellar space at speeds of millions of miles per hour. The images of the Crab Nebula and 3C58 show how extremely dense, rapidly rotating neutron stars produced when a massive star explodes can create clouds of high-energy particles light years across that glow brightly in X-rays.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

