CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
X-ray & Optical Images of R Aquarii
These images show Chandra X-ray data as well as optical data of the "symbiotic" system R Aquarii (R Aqr). This system contains a white dwarf star in orbit with a pulsating red giant. Occasionally, the white dwarf pulls enough material from the red giant onto its surface to generate a thermonuclear explosion. Since shortly after Chandra launched in 1999, astronomers have been using the X-ray telescope to monitor the behavior of R Aqr, giving them a better understanding of the behavior of this volatile stellar pair.
(X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/R. Montez et al.; Optical: Adam Block/Mt. Lemmon SkyCenter/U. Arizona)
These images show Chandra X-ray data as well as optical data of the "symbiotic" system R Aquarii (R Aqr). This system contains a white dwarf star in orbit with a pulsating red giant. Occasionally, the white dwarf pulls enough material from the red giant onto its surface to generate a thermonuclear explosion. Since shortly after Chandra launched in 1999, astronomers have been using the X-ray telescope to monitor the behavior of R Aqr, giving them a better understanding of the behavior of this volatile stellar pair.
(X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/R. Montez et al.; Optical: Adam Block/Mt. Lemmon SkyCenter/U. Arizona)
2
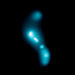
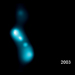
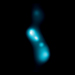
Chandra X-ray Images of R Aquarii in 2000, 2003, 2005
As astronomers have made observations of R Aqr with Chandra over the years, in 2000, 2003, and 2005, they have seen changes in this jet. Specifically, blobs of X-ray emission are moving away from the stellar pair at speeds of about 1.4 million and 1.9 million miles per hour. Despite travelling at a slower speed than the material ejected by the nova, the jets encounter little material and do not slow down much. On the other hand, matter from the nova sweeps up a lot more material and slows down significantly, explaining why the rings are not much larger than the jets.
(NASA/CXC/SAO/R. Montez et al.;)
Animation/Video
As astronomers have made observations of R Aqr with Chandra over the years, in 2000, 2003, and 2005, they have seen changes in this jet. Specifically, blobs of X-ray emission are moving away from the stellar pair at speeds of about 1.4 million and 1.9 million miles per hour. Despite travelling at a slower speed than the material ejected by the nova, the jets encounter little material and do not slow down much. On the other hand, matter from the nova sweeps up a lot more material and slows down significantly, explaining why the rings are not much larger than the jets.
(NASA/CXC/SAO/R. Montez et al.;)
Animation/Video
R Aquarii (June 6, 2017)