X-ray View of a Young Planetary Nebula
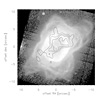
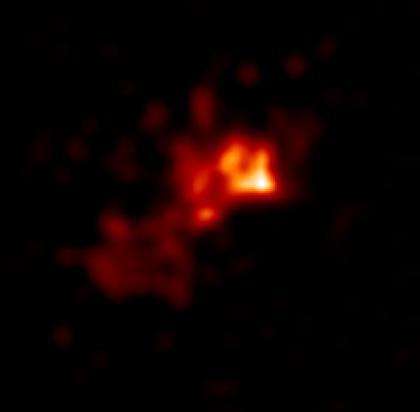
Chandra's image of NGC 7027 represents the first detection of X-rays from this young planetary nebula that is about 3,000 light years from Earth. A bubble of 3 million degree Celsius gas with a length about a hundred times that of our solar system is shown in the image. The image is brighter to the upper right – the side of the nebula nearest the Earth – where there is less obscuring material to block the X-ray emission.
NGC 7027 is the remains of a Sun-like star that has ejected much of its mass to expose its hot core. The X-rays are thought to be produced when a "fast" wind from the hot core collides with the "slow" wind that was ejected earlier during the star's red giant phase. This collision heats the matter to several million degrees so that it glows in X-rays.
Chandra data suggest that there is an overabundance of helium, carbon, nitrogen, magnesium, and silicon present in NGC 7027. This is consistent with theories that predict that planetary nebulas seed interstellar space with "heavy" elements (that is, any element heavier than hydrogen and helium) produced by nuclear reactions during the evolution of the star.
These observations were made by a team of scientists led by Joel Kastner of the Rochester Institute of Technology.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Chandra X-ray Observatory image shows a planetary nebula named NGC 7027, which is a type of celestial object formed when a sun-like star dies and its outer layers are ejected into space. The dominant colors in the image are red and orange. Chandra's image of NGC 7027 represents the first detection of X-rays from this young planetary nebula that is about 3,000 light years from Earth. A bubble of 3 million degree Celsius gas with a length about a hundred times that of our solar system is shown in the image. The image is brighter to the upper right - the side of the nebula nearest the Earth - where there is less obscuring material to block the X-ray emission.